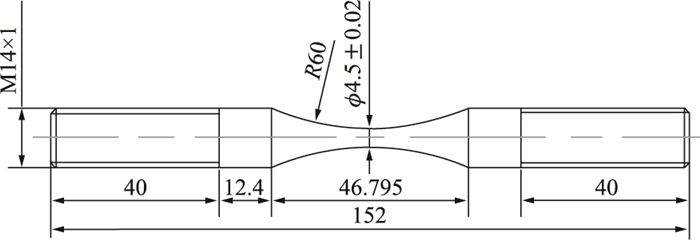
Fatiguelife prediction model of carburized gear steel based on cumulative damage
-
摘要: 采用轴向高频疲劳试验机进行超高周疲劳实验,研究了不同应力比(R=0和R=0.3)下渗碳齿轮钢疲劳特性。结果表明:在应力比为0和0.3时,渗碳齿轮钢的失效形式分为表面失效和内部失效。内部失效过程分为疲劳裂纹萌生阶段(夹杂-细颗粒区(fine granular area, FGA))、稳定扩展阶段(FGA-鱼眼)和瞬间断裂(鱼眼之外)。基于累积损伤法,建立了内部裂纹萌生和扩展阶段的疲劳寿命预测模型;最终建立了渗碳齿轮钢多应力比下的全寿命预测模型,预测精度较高。Abstract: Very high cycle fatigue tests were carried out on the axial high-frequency fatigue testing machine. The fatigue characteristics of carburized gear steel under different stress ratios (R=0 and R=0.3) were studied. The results show that when the stress ratio is 0 and 0.3, the failure modes of carburized gear steel are divided into surface failure and interior failure. The interior failure process is divided into fatigue crack initiation stage (from inclusion to fine granular area (FGA)), stable propagation stage (from FGA to fisheye) and instantaneous fracture (outside fisheye). Based on the cumulative damage method, the life prediction models of interior crack initiation and propagation stages are established, respectively. Finally, the fatigue life prediction model of carburized gear steel is established, prediction accuracy is higher.
-
Key words:
- carburized gear steel /
- crack size /
- residual stress /
- initiation-propagation /
- life prediction
-
表 1 齿轮钢的化学成分
% C Si Mn S P Cr Ni Fe 0.16 0.37 0.6 0.035 0.035 1.65 3.65 其他 表 2 全寿命预测模型拟合参数评估
R mi ni mp np 0 7.62 -1.43 -0.54 7.42 0.3 6.00 0.27 -4.92 16.90 表 3 疲劳寿命预测结果
应力比 应力幅 NT/Nexp R=0 500 1.24 R=0 525 1.16 R=0 550 0.34 R=0 550 0.44 R=0 575 1.12 R=0 600 1.89 R=0 575 2.85 R=0 625 2.89 R=0.3 455 1.05 R=0.3 437.5 1.29 -
[1] Deng H L, Liu H, Liu Q C, et al. Fatigue strength prediction of carburized 12Cr steel alloy: Effects of evaluation of maximum crack sizes and residual stress distribution[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2020, 43(2): 342-354. doi: 10.1111/ffe.13149 [2] Sheng J, Huang S, Zhou J Z, et al. Effects of warm laser peening on the elevated temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior of IN718 nickel-based superalloy[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 169: 99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2016.11.016 [3] Han S W, Yang X G, Shi D Q, et al. Microstructure-sensitive modeling of competing failure mode between surface and internal nucleation in high cycle fatigue[J]. International Journal of Plasticit, 2020, 126: 102622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.11.001 [4] Fintová S, Kuběna I, Trško L, et al. Fatigue behavior of AW7075 aluminum alloy in ultra-high cycle fatigue region[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2020, 774: 138922. [5] Deng H L, Liu H, Liu Q C, et al. Fatigue strength prediction of carburized 12Cr steel alloy: effects of evaluation of maximum crack sizes and residual stress distribution[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2020, 43(2): 342-354. [6] Kong W W, Yuan C, Zhang B N. Investigations on cyclic deformation behaviors and corresponding failure modes of a Ni-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2020, 791: 139775. [7] 黄朝文, 赵永庆, 辛社伟, 等. 显微组织均匀性对片层Ti-55531齿轮高周疲劳裂纹萌生的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(3): 663-668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201703016.htm [8] 邓海龙, 李伟, 孙振铎, 等. 基于夹杂-细晶粒区-鱼眼疲劳失效的超长寿命预测模型[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017, 39(4): 567-573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201704012.htm [9] Zhu M L, Jin L, Xuan F Z. Fatigue life and mechanistic modeling of interior micro-defect induced cracking in high cycle and very high cycle regimes[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 157: 259-275. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.036 [10] Sakai T, Oguma N, Morikawa A. Microscopic and nanoscopic observations of metallurgical structures around inclusions at interior crack initiation site for a bearing steel in very high‐cycle fatigue[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2015, 38(11): 1305-1314. doi: 10.1111/ffe.12344 [11] Hong Y S, Lei Z Q, Sun C Q, et al. Propensities of crack interior initiation and early growth for very-high-cycle fatigue of high strength steels[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2014, 58: 144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.02.023 [12] Murakami Y, Endo M. Effects of defects, inclusions and inhomogeneities on fatigue strength[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1994, 16(3): 163-182. doi: 10.1016/0142-1123(94)90001-9 [13] Wang Q Y, Berard J Y, Dubarre A, et al. Gigacycle fatigue of ferrous alloys[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 1999, 22(8): 667-672. [14] Sun C Q, Liu X L, Hong Y S. A two-parameter model to predict fatigue life of high-strength steels in a very high cycle fatigue regime[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2015, 31(3): 383-391. doi: 10.1007/s10409-015-0451-4 [15] Hou S Q, Xu J Q. Relationship among S-N curves corresponding to different mean stresses or stress ratios[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A(Applied Physics & Engineering), 2015, 16(11): 885-893. http://www.jzus.zju.edu.cn/oldversion/opentxt.php?doi=10.1631/jzus.A1400321 [16] Sakai T. Review and Prospects for Current Studies on Very High Cycle Fatigue of Metallic Materials for Machine Structural Use[J]. The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2009, 3(3): 425-439. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039731005510_ba93.html [17] 韩培培, 权纯逸, 焦清洋, 等. 激光冲击强化对7050-T7451铝齿轮残余应力和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(2): 190-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSRC202102039.htm -




 下载:
下载: