Research status of deformation damage behavior of high strength metastable β titanium alloys
-
摘要: 亚稳β钛合金具有密度小、比强度高、可塑性好以及优良的耐腐蚀等力学和物理学性能,已经广泛应用在航空航天、生物医学和石油化工等领域。为实现对新一代高强度、高塑性钛合金的研发与应用,必须明确亚稳β钛合金力学性能与其变形损伤行为之间的联系。文章分析了亚稳β钛合金在变形损伤过程中的组织演变,概述了亚稳β钛合金的各种变形行为及各变形之间的联系,总结了不同的变形行为影响下对亚稳β合金力学性能的提升;然后阐述了亚稳β钛合金在动载荷下的损伤行为及其内部的组织演变,探讨了微观损伤对合金强化与失效之间的联系,以期对新型钛合金的研发与优化提出新见解。Abstract: Metastable β titanium alloy has mechanical and physical properties such as low density, high specific strength, good plasticity and excellent corrosion resistance, and has been widely used in aerospace, biomedicine, petrochemical and other fields. In order to realize the development and application of a new generation of high-strength and high-plastic titanium alloys, the relationship between the mechanical properties of metastable β titanium alloys and their deformation damage behavior must be clarified. In this paper, the microstructure evolution of metastable β titanium alloys in the process of deformation damage is analyzed, the various deformation behaviors of metastable β titanium alloys and the relationship between each deformation are summarized, and the improvement of the mechanical properties of metastable β alloys under the influence of different deformation behaviors is summarized. Then, the damage behavior and internal microstructure evolution of metastable β titanium alloys under dynamic load are expounded, and the relationship between microscopic damage and alloy strengthening and failure is discussed, in order to put forward new insights into the development and optimization of new titanium alloys.
-
Key words:
- metastable β titanium alloy /
- deformation behavior /
- damage behavior
-
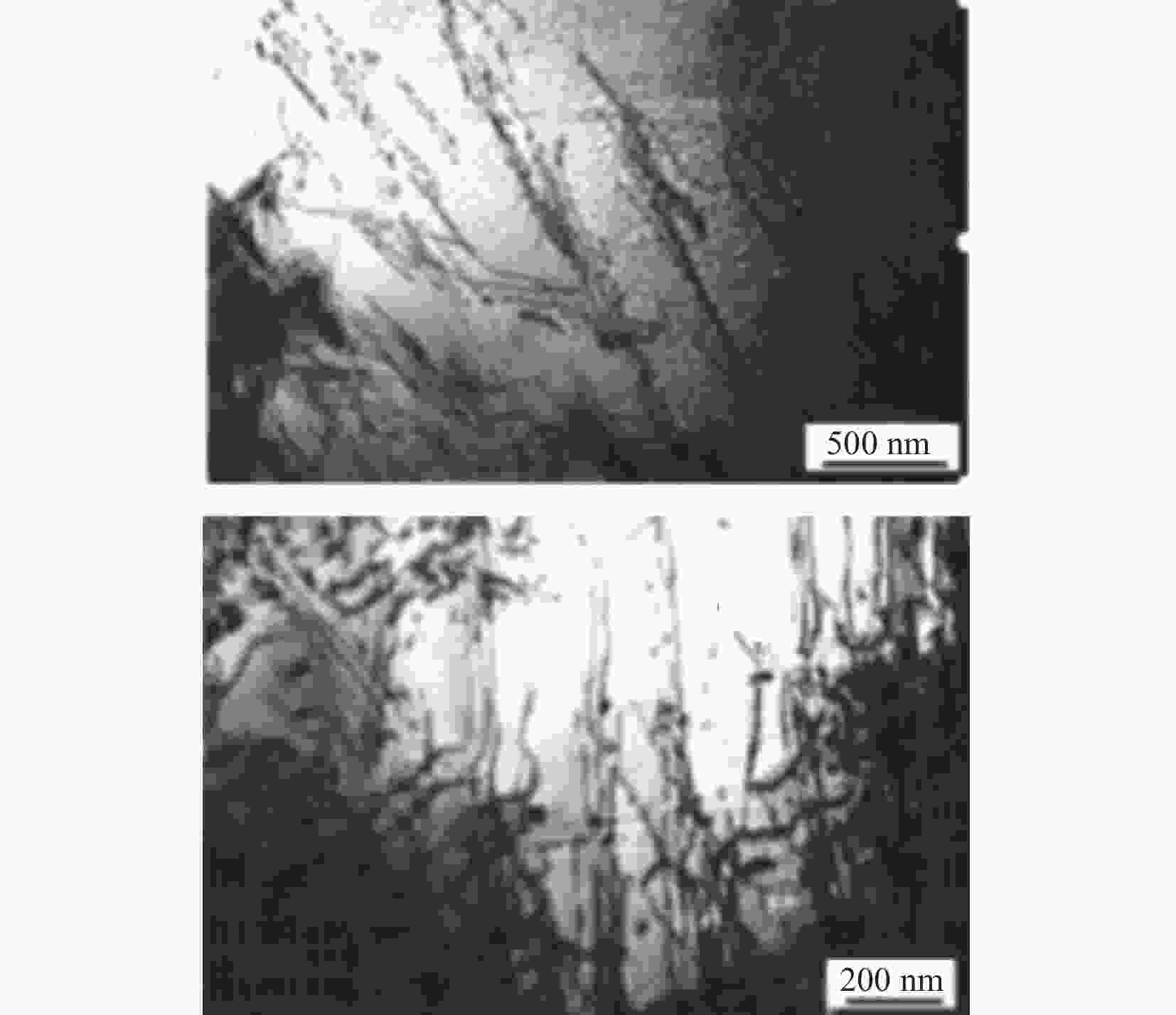
图 2 双光束TEM明场像显示Ti-30V-15Cr-2Al钛合金室温形变样品内的位错缠结[15]
图 3 冲击载荷变形过程中的微观组织演变[23]
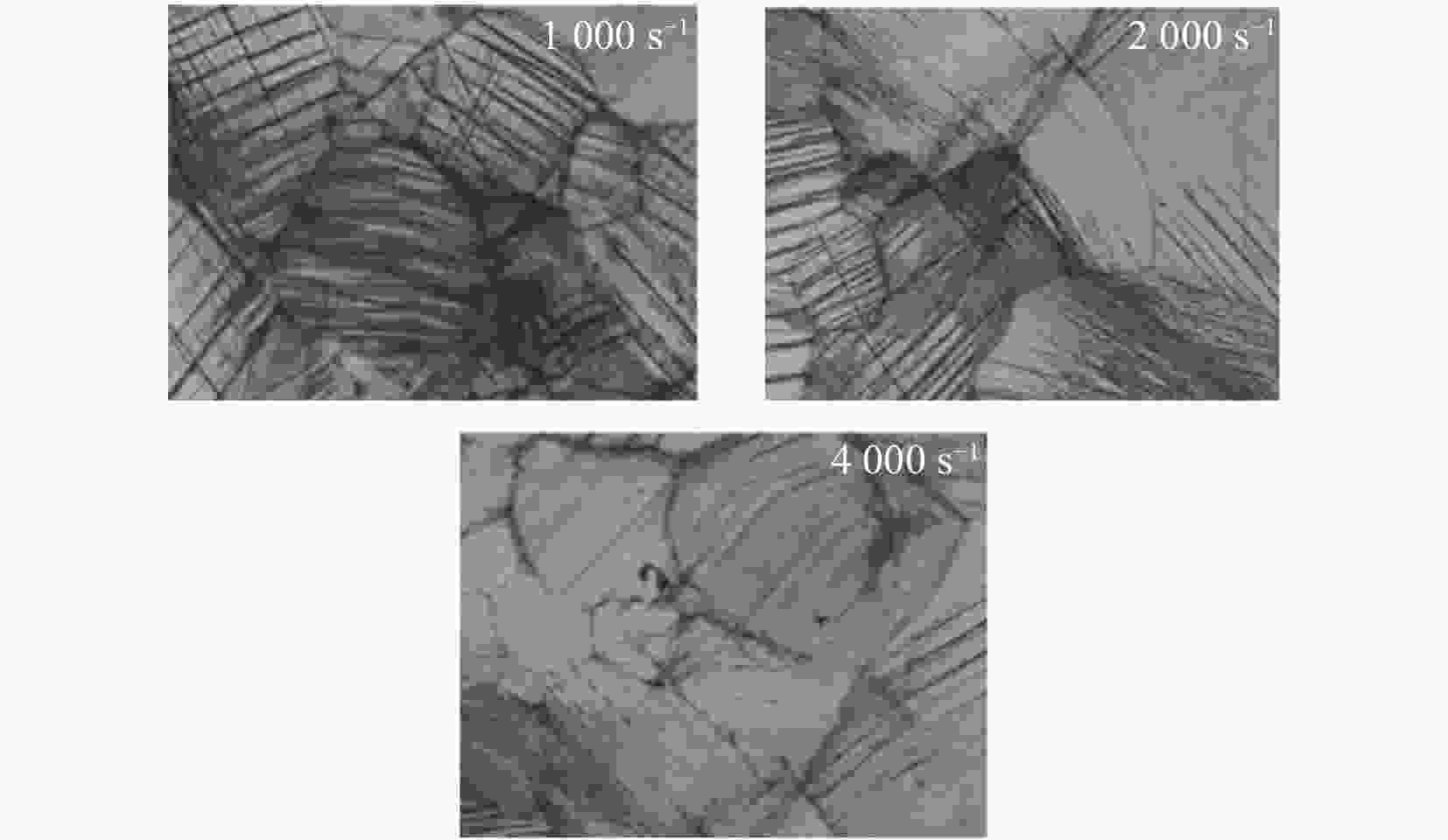
图 4 不同应变速率的Ti-1023合金的EBSD能带对比[24]
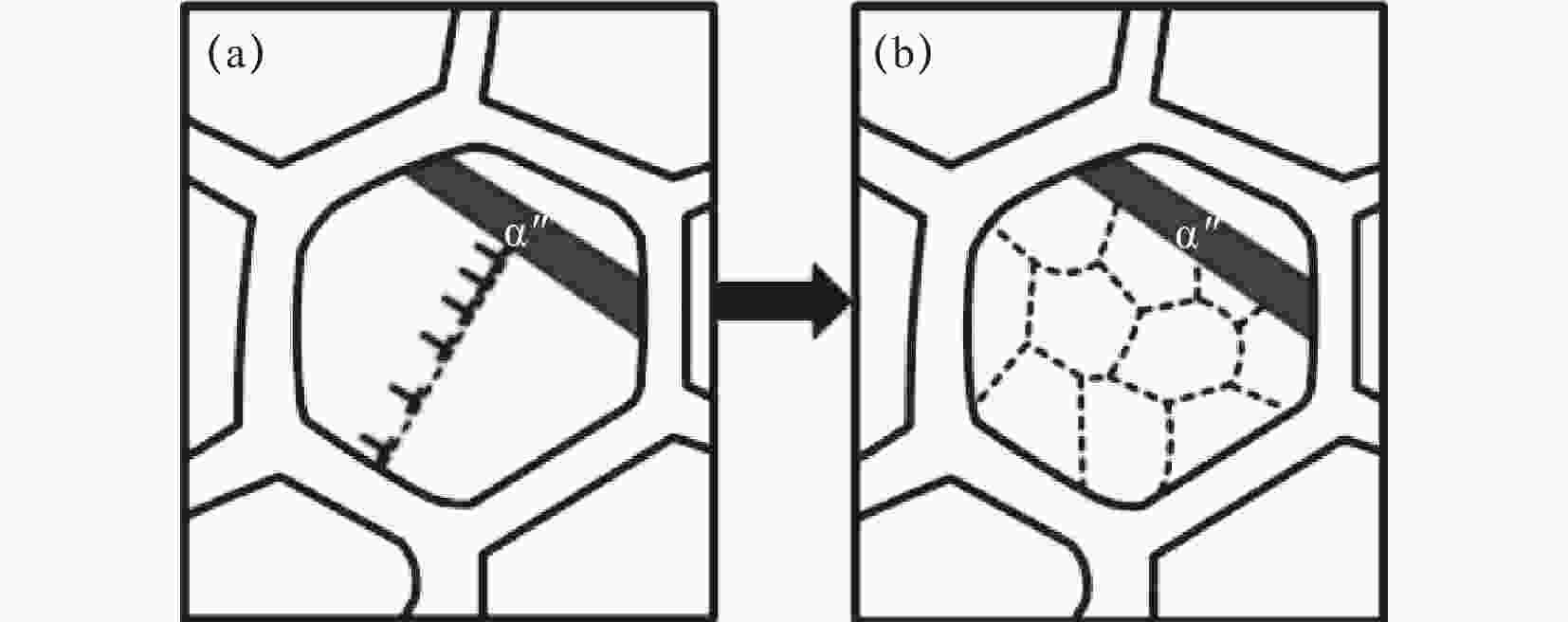
图 5 针状α''马氏体的晶粒细化演变[26]
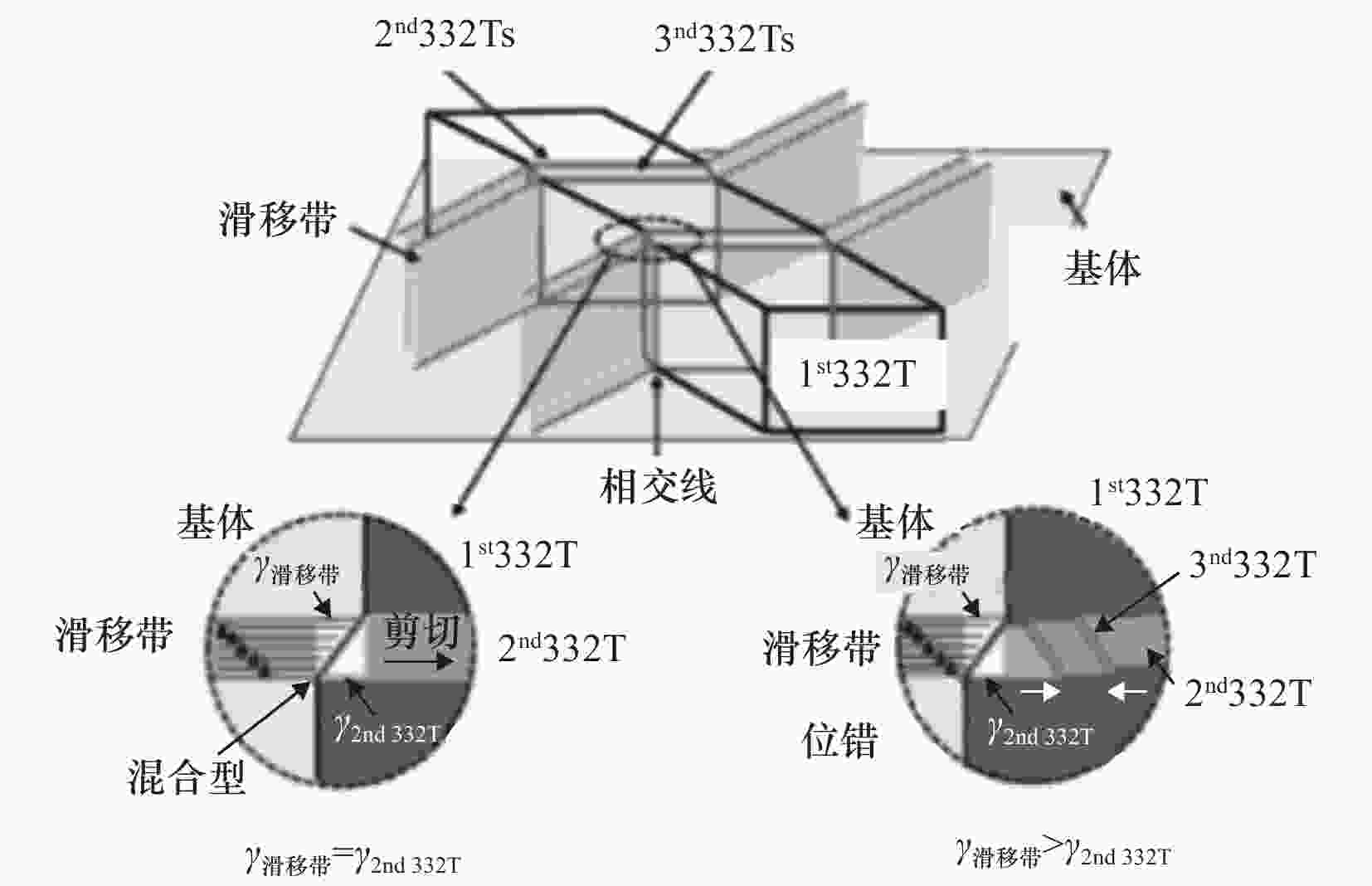
图 6 多级孪晶体系的形成顺序的3D视图和剖视图[28]
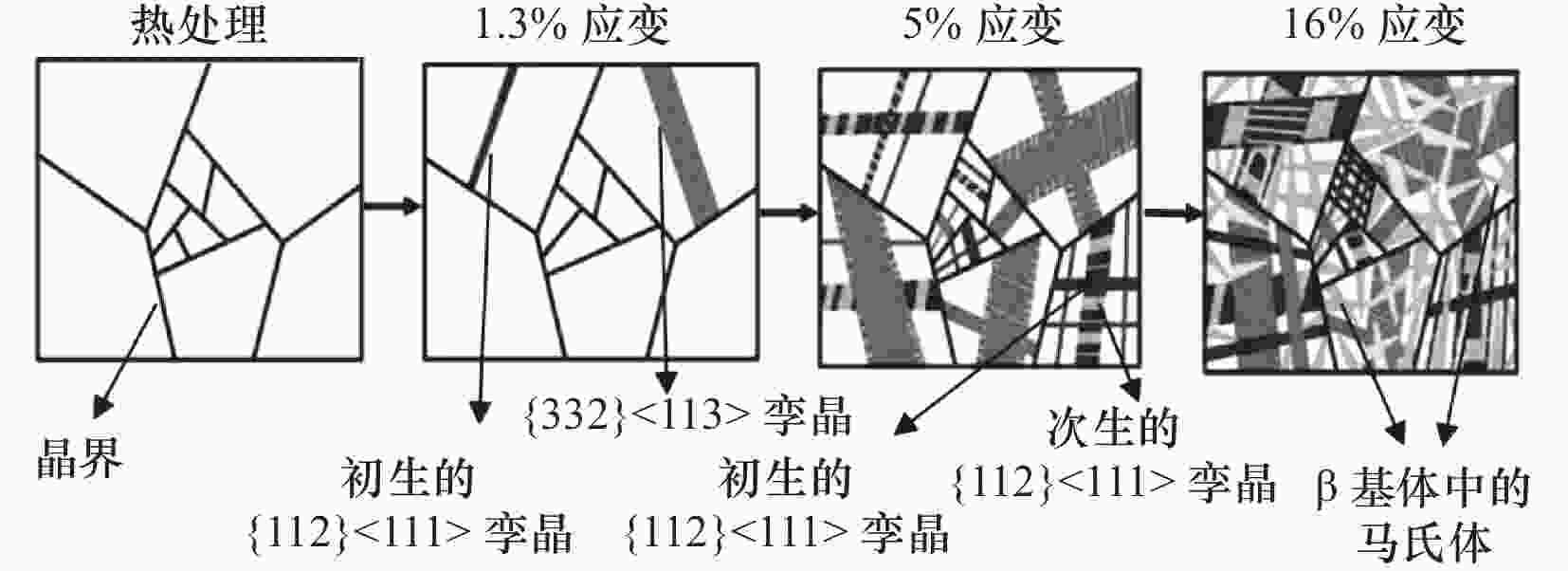
图 7 Ti-7Mo-3Cr合金随应变增加时的微观结构演变[29]
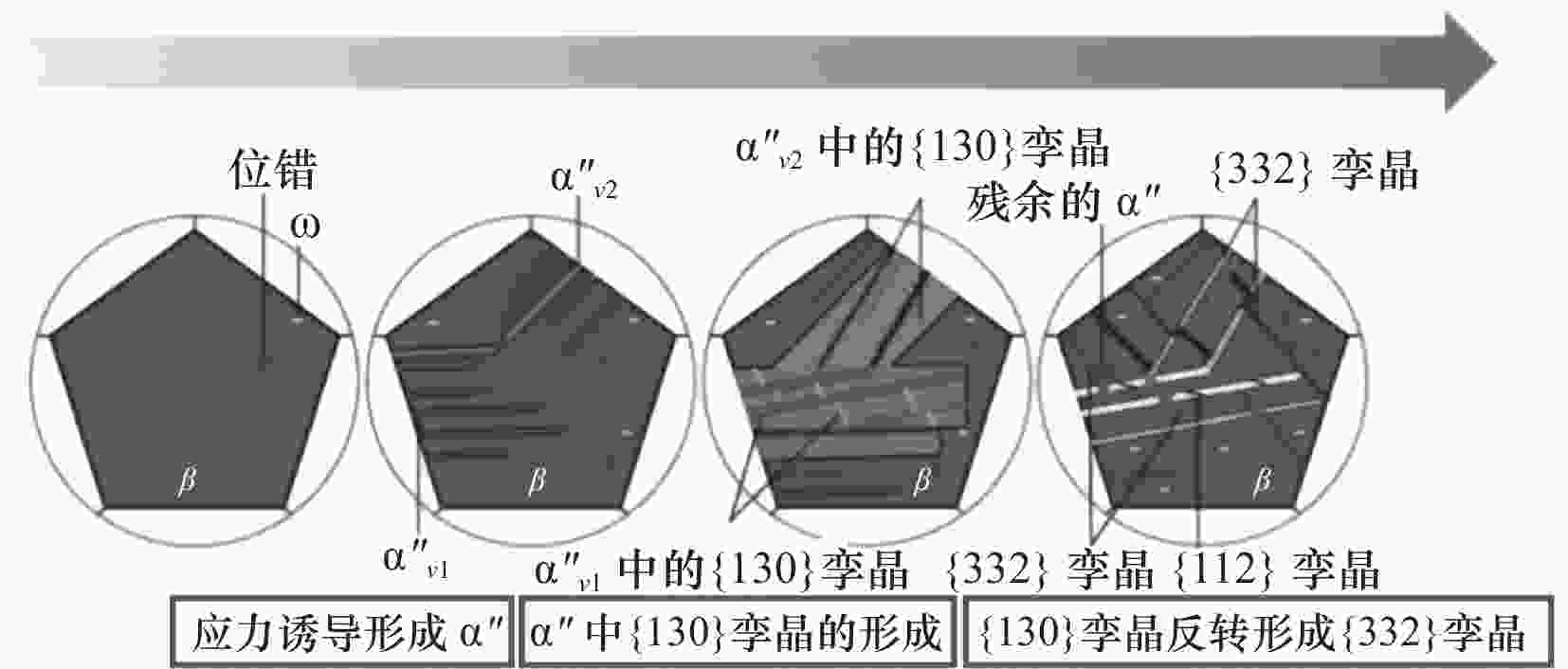
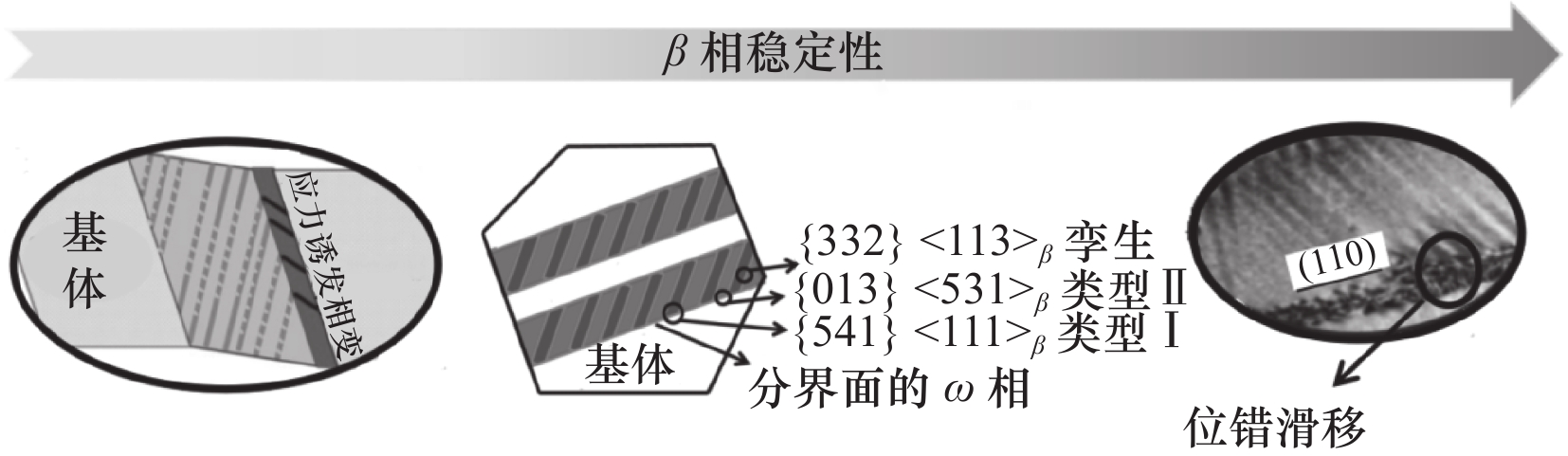
图 8 亚稳β钛合金中应力诱发马氏体和{332}孪晶的耦合[35]
图 9 层状显微组织Ti-54432合金在拉伸过程中的裂纹扩展[38]
图 10 孔洞汇聚与裂纹的扩展[39]
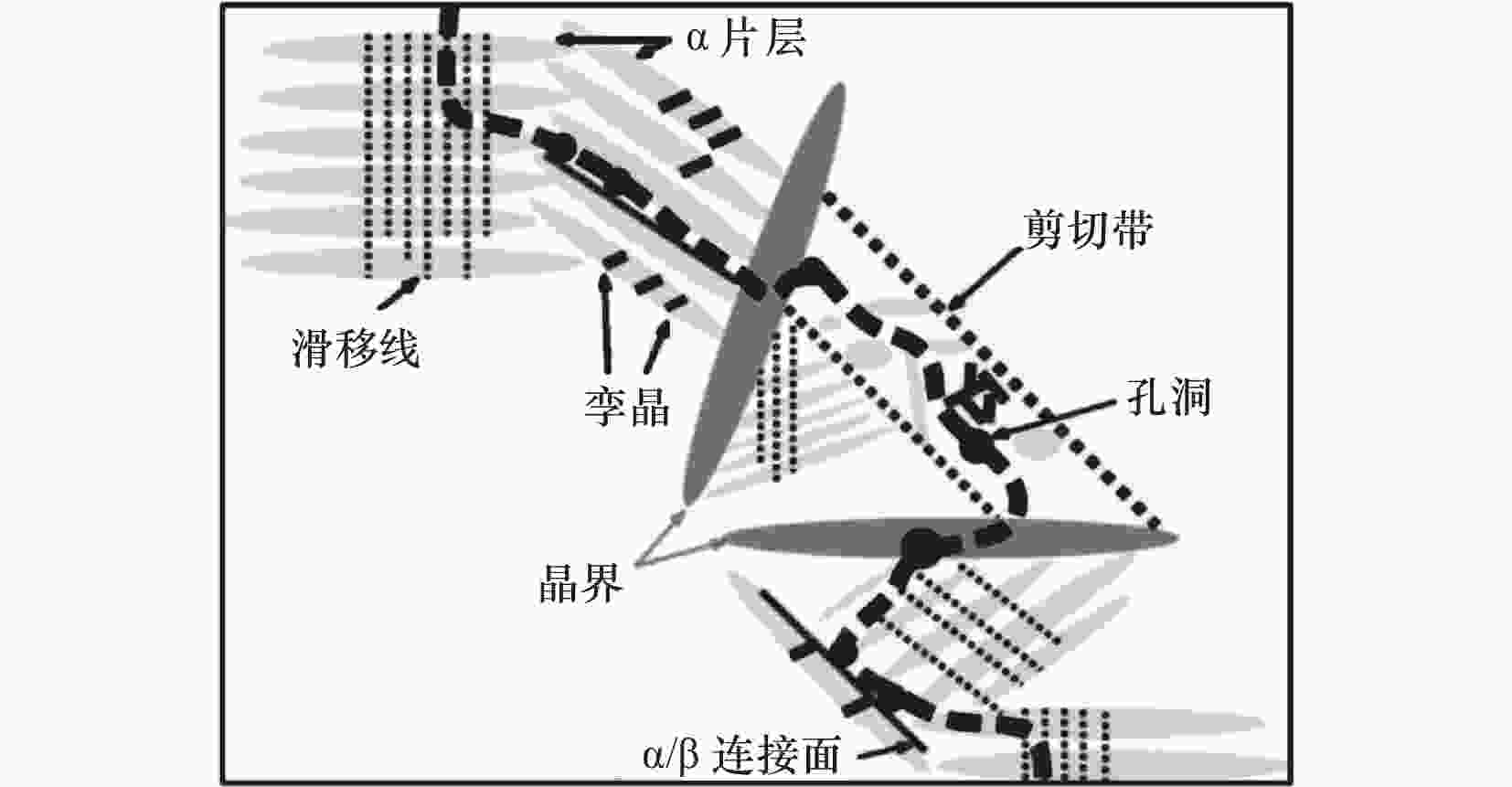
图 11 ASB中的裂纹演化[41]
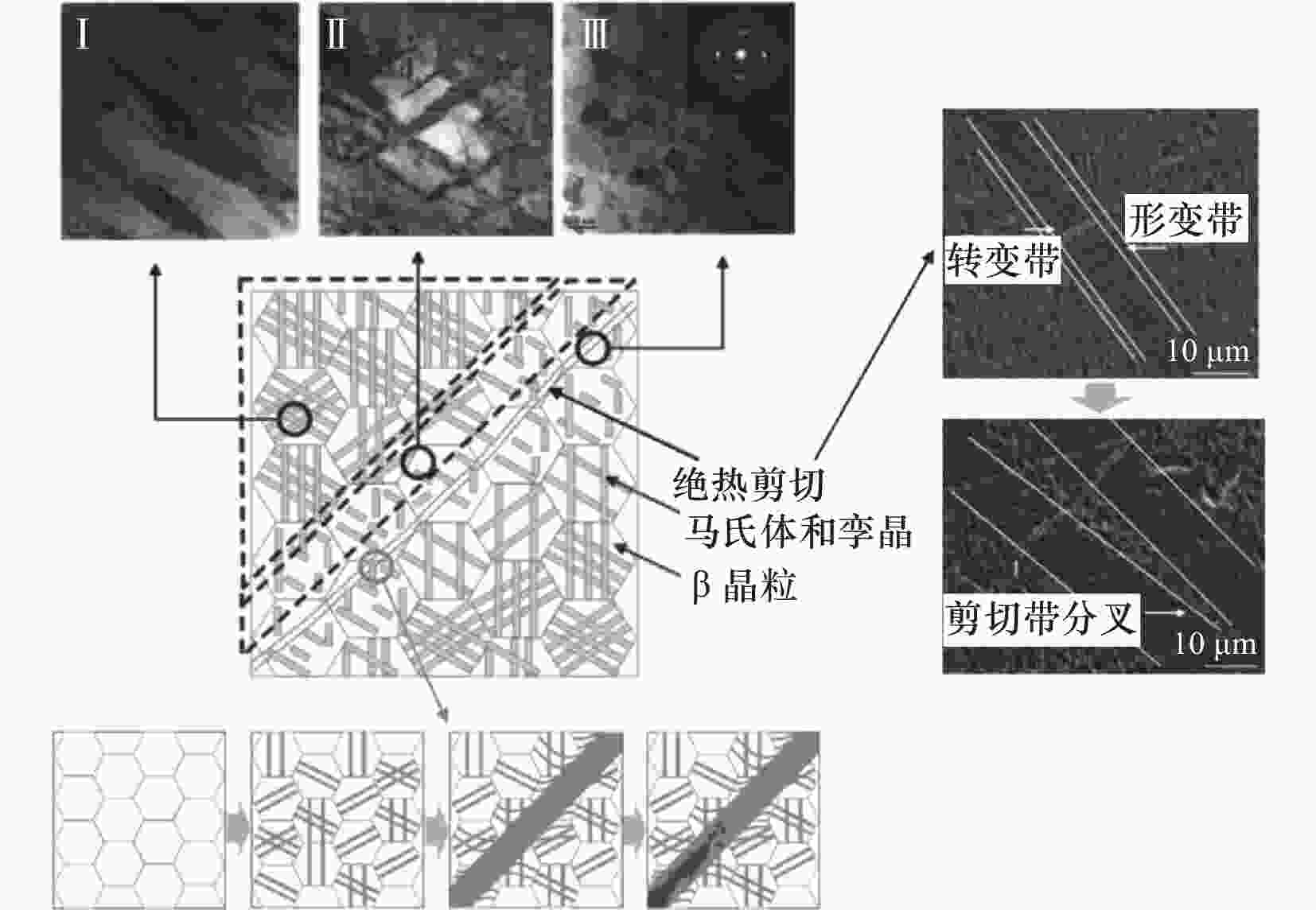
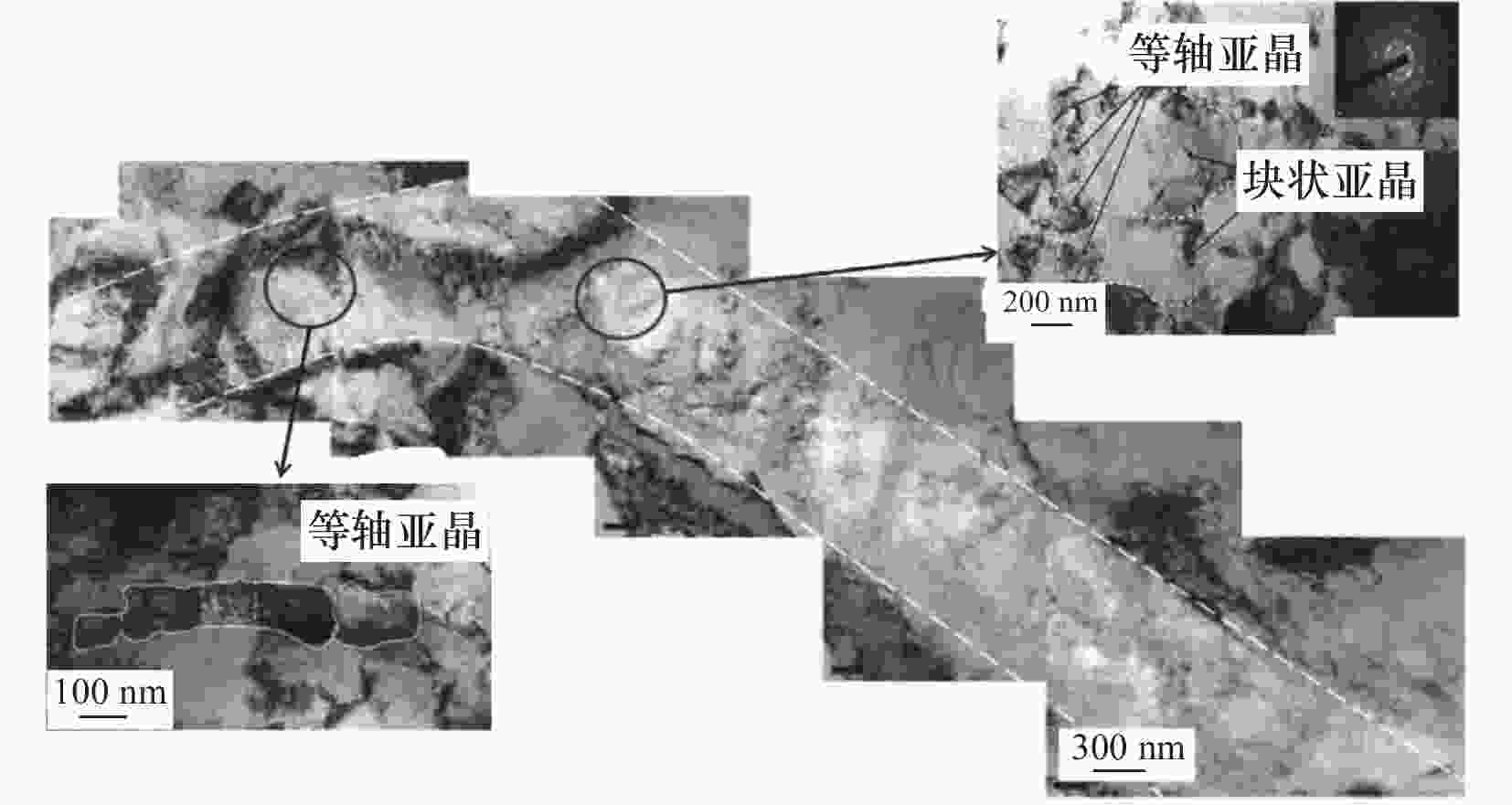
图 13 绝热剪切带内的微观结构[46]
学者 理论 模型 内容 示意图 Richman R[18] 剪切与重组
机制{332}孪晶结构模型 基于刚性球模型假设说明了{332}孪晶结构的形成,但在孪晶/基体界面易产生晶格畸变,形成高的界面能。 
Takemoto Y[19] 松弛重组 ${\text{β}} \mathbin{\lower.3ex\hbox{$\buildrel\textstyle\rightarrow\over{\smash{\leftarrow}\vphantom{_{\vbox to.5ex{\vss}}}}$}}{\text{α}} $''马氏体机制 改进了Richman模型的高界面能缺点,同时说明{332}孪晶是由α''相转变而来,而α''相是由基体产生。 
Kawabata T[20] 位错机制 位错-孪晶
模型说明{332}孪晶来自位错分解和不全位错的
滑移,进而说明位错过程中发生了原子的
重组。
Tobe H[21] 晶格不稳定性 基于原子对移动的{332}孪晶结构模型 基于晶体学说明了{332}孪晶结构的形成,但此理论难于说明微观组织的形成。 
-
[1] 陈玮,刘运玺,李志强. 高强β钛合金的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 航空材料学报,2020,40(3):63-76. [2] 杨冬雨,付艳艳,惠松骁,等. 高强高韧钛合金研究与应用进展[J]. 稀有金属,2011,35(4):575-580. [3] Banerjee D,Williams J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology[J]. Acta Materialia,2013,61(3):844-879. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.10.043 [4] Ren L,Xiao W,Kent D,et al. Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility in a metastable β-Ti alloy by stress-induced hierarchical twin structure[J]. Scripta Materialia,2020,184:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.03.039 [5] Zhao G H,Xu X,Dye D,et al. Microstructural evolution and strain-hardening in TWIP Ti alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2020,183:155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.11.009 [6] Kolli R P,Devaraj A. A review of metastable beta titanium alloys[J]. Metals,2018,8(7):506. doi: 10.3390/met8070506 [7] Sun F,Zhang J Y,Marteleur M,et al. Deformation mechanisms in a metastable β titanium alloy showing combine[J]. Acta Materialia,2013,61(17):6406. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.07.019 [8] Mantri S A,Sun F,Choudhuri D,et al. Deformation induced hierarchical twinning coupled with omega transformation in a metastable β-Ti alloy[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):1334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37865-0 [9] Yang Y,Castany P,Hao Y L,et al. Plastic deformation via hierarchical nano-sized martensitic twinning in the metastable β Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy[J]. Acta Materialia,2020,194:27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.021 [10] Zhu W,Tan C,Xiao R,et al. Slip behavior of Bi-modal structure in a metastable β titanium alloy during tensile deformation[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2020,57:188-196. [11] 赖敏杰,李金山. 亚稳β钛合金的变形孪晶和应力诱发相变[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2019,29(9):2185-2191. [12] Zafari A,Wei X S,Xu W,et al. Formation of nanocrystalline β structure in metastable beta Ti alloy during high pressure torsion:the role played by stress induced martensitic transformation[J]. Acta Materialia,2015,97:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.06.042 [13] Hua K,Zhang Y,Gan W,et al. Hot deformation behavior originated from dislocation activity and β to α phase transformation in a metastable β titanium alloy[J]. International Journal of Plasticity,2019,119:200-214. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.03.011 [14] Zhang J,Sun F,Chen Z,et al. Strong and ductile beta Ti–18Zr–13Mo alloy with multimodal twinning[J]. Materials Research Letters,2019,7(6):251-257. doi: 10.1080/21663831.2019.1595763 [15] Li Y G,Blenkinsop P A,Loretto M H,et al. Effect of aluminium on deformation structure of highly stabilised β-Ti–V–Cr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology,1999,15(2):151-155. doi: 10.1179/026708399101505680 [16] Huang X,Li J S,Lai M J. Influences of grain size on the deformation behavior of a twinning-induced plasticity metastable β titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2023,937:168274. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168274 [17] Blackburn M J,Feeny J A. Stress-induced transformations in Ti-Mo alloys[J]. Journal of the Institute of Metals,1971,99:132-134. [18] Richman R. Deformation twinning[M].USA: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers,1964. [19] Takemoto Y,Hida M,Sakakibara A. Change of deformation mode caused by aging of Ti-14 mass%Mo alloy single crystals and embrittlement mechanism due to the ω-phase[J]. Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals,1989,53(10):1004-1012. [20] Kawabata T,Kawasaki S,Izumi O. Mechanical properties of Ti-Nb-Ta single crystals at cryogenic temperatures[J]. Acta Materialia,1998,46(8):2705-2715. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00475-8 [21] Tobe H,Kim H Y,Inamura T,et al. Hierarchical {332}<113> twinning in a metastable β Ti-alloy showing tolerance to strain localization Journal[J]. Materials Research Letters. 2020,8(7),247. [22] Castany P,Yang Y,Bertrand E,Gloriant T. Reversion of a parent {130}<310>{α''} martensitic twinning system at the origin of {332}<113>{β} twins observed in metastable β titanium alloys[J]. Physical Review Letters,2016,117(24). [23] An X L,Jiang W T,Ni S,et al. Origin of {332}<113> twinning and twin-twin intersections in a shock load metastable β Ti-12Mo alloy[J]. Materials Characterization,2023:112674. [24] Ma X K,Li J H,Chen Z,et al. Abnormal work hardening in a TRIP-assisted metastable β titanium alloy under high strain rate loading[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2022:838. [25] Zhao X L,Wang Y,Xue H,et al. The effect of strain rate on deformation-induced α′ phase transformation and mechanical properties of a metastable β-type Ti–30Zr–5Mo alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022:894. [26] Zafari A,Xia K. Progress in severe plastic deformation of metastable beta Ti alloys[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,2020,22(1):201900471. [27] Chen K,Fan Q B,Yang L,et al. A novel sequential mechanism associated with stress-induced β→ω→β+α phase transformation in Ti–6Mo-3.5 Cr–1Zr titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2022:849. [28] Zhang J Y,Fu Y Y,Wu Y J,et al. Hierarchical {332}< 113> twinning in a metastable β Ti-alloy showing tolerance to strain localization[J]. Materials Research Letters,2020,8(7):247-253. doi: 10.1080/21663831.2020.1745920 [29] Gao J H,Huang Y H,Guan D K,et al. Deformation mechanisms in a metastable beta titanium twinning induced plasticity alloy with high yield strength and high strain hardening rate[J]. Acta Materialia,2018,152:301-314. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.04.035 [30] Xing H,Sun J. Mechanical twinning and omega transition by <111> {112} shear in a metastable beta titanium alloy[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2008,93(3):031908. doi: 10.1063/1.2959183 [31] Lai M J,Tasan C C,Raabe D. On the mechanism of {332} twinning in metastable β titanium alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2016,111:173-186. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.03.040 [32] Hanada S,Izumi O. Correlation of tensile properties,deformation modes,and phase stability in commercial β-phase titanium alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,1987,18:265-271. doi: 10.1007/BF02825707 [33] Marteleur M,Sun F,Gloriant T,et al. On the design of new β-metastable titanium alloys with improved work hardening rate thanks to simultaneous TRIP and TWIP effects[J]. Scripta Materialia,2012,66(10):749-752. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.01.049 [34] Fu Y,Xiao W,Kent D,et al. Ultrahigh strain hardening in a transformation-induced plasticity and twinning-induced plasticity titanium alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia,2020,187:285-290. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.06.029 [35] Xiao J F,He B B,Tan C W. Effect of martensite on {332} twinning formation in a metastable beta titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022:895. [36] Gao M,Guo E,Chen Z,et al. Revealing the role of micropore defects in tensile deformation of a B4Cp/Al composite using an actual three-dimensional model[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2023,22:3146-3155. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.12.145 [37] Curran D R,Seaman L,Shockey D A. Dynamic failure in solids[J]. Physics Today,1977,30(1):46-55. doi: 10.1063/1.3037367 [38] Wang J,Zhao Y Q,Zhou W,et al. In-situ study on tensile deformation and damage evolution of metastable β titanium alloy with lamellar microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2021,824:141790. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141790 [39] Qin D Y,Miao Y G,Li Y L. Formation of adiabatic shearing band for high-strength Ti-5553 alloy:A dramatic thermoplastic microstructural evolution[J]. Defence Technology,2022,18(11):2045-2051. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.06.010 [40] Wang J,Zhao Y Q,Zhao Q Y,et al. Comparison on impact toughn-ess of high-strength metastable β titanium alloy with bimoda-l and lamellar microstructures[J]. Metals,2022,12(2):271. doi: 10.3390/met12020271 [41] Liu X,Zhou Y,Zhu X J,et al. The failure mechanism at adiabatic shear bands of titanium alloy:high-precision survey using precession electron diffraction and geometrically necessary dislocation density calculation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2019,746:322-331. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.016 [42] Yang H L,Wang D D,Zhu X J,et al. Dynamic compression-induced twins and martensite and their combined effects on the adiabatic shear behavior in a Ti-8.5Cr-1.5Sn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2019,759:203-209. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.05.040 [43] 易湘斌,张俊喜,李宝栋,等. 高温、高应变率下TB6钛合金的动态压缩性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程,2019,48(4):1220-1224. [44] Chen K,Fan Q B,Yang L,et al. Deciphering the microstructural evolution and adiabatic shearing behavior of the titanium alloy with stress-induced ω phase transformation during dynamic compression[J]. Materials & Design,2022,221:110939. [45] Dai J C,Min X H,Wang L. Dynamic response and adiabatic shear behavior of β-type Ti–Mo alloys with different deformation modes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A,2022,857:144108. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.144108 [46] Zhan H Y,Zeng W D,Wang G,et al. Microstructural characteristics of adiabatic shear localization in a metastable beta titanium alloy deformed at high strain rate and elevated temperatures[J]. Materials Characterization,2015,102:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2015.02.017 [47] Rittel D,Landau P,Venkert A. Dynamic recrystallization as a potential cause for adiabatic shear failure[J]. Physical Review Letters,2008,101(16):165501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.165501 -




 下载:
下载: